3D Open Vocabulary Semantic Segmentation for Robot Navigation
1. Introduction
VLMaps is a spatial map representation that embeds pretrained visual-language features with a 3D reconstruction and projects to a top-down 2D map. VLMaps embeds pixel-level visual features from an LSeg visual encoder to points in a point cloud. These points are then projected to a top-down navigation map where only the point with the highest height is kept. After this, the visual features are compared through cosine similarity to textual features from a CLIP text encoder to determine the semantic label of the point. CLIPs amazing visual-language feature space allows us to know which visual features are "closest" to the language feature we are interested in. In other words, whatever classes ("chair", "floor", ... etc.) we can know per pixel or voxel in our case, what "word" or "class" that pixel/voxel is closest to. In the original work, due to the top-down projection, the robot wouldn't be capable of 3D navigation such as “go to the plant below the table.” Addressing this problem was our main goal with this project. We used the Matterport3D Dataset.2. Approach
To address this limitation, I implemented a voxelization algorithm that iterates through all Matterport scans of a scene and builds the voxel grid incrementally. The voxel grid is a dictionary where each key corresponds to a voxel coordinate (vx, vy, vz) and each value is a voxel object containing its coordinates, color, and semantic features. For each Matterport3D scene scan, RGB, depth, and camera intrinsic/extrinsic parameters are loaded. Using the camera intrinsics, the depth map is converted to the camera coordinate frame to make a local point cloud. These points are then transformed into the world coordinate frame using the camera extrinsics to make the global point cloud. In parallel, the RGB image is processed by the LSeg Visual Encoder and embeds pixel features to each point. These pixel features are compared to LSeg Text Encoder text features and assigned a cosine similarity score to generate a point semantic embeddings. The corresponding voxel is then updated with the point's color and semantic features. When multiple points fall into the same voxel, I average all their embeddings to generate a singular embedding.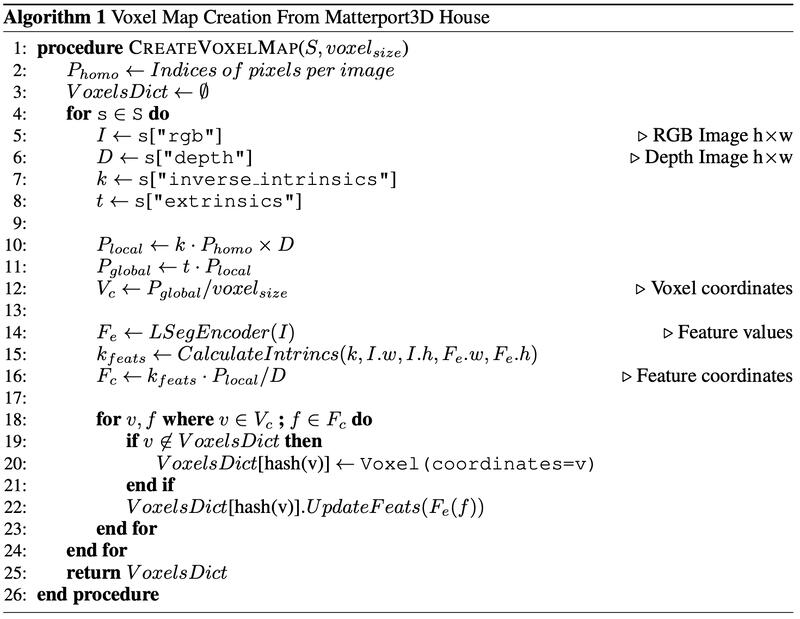
Voxelization Algorithm
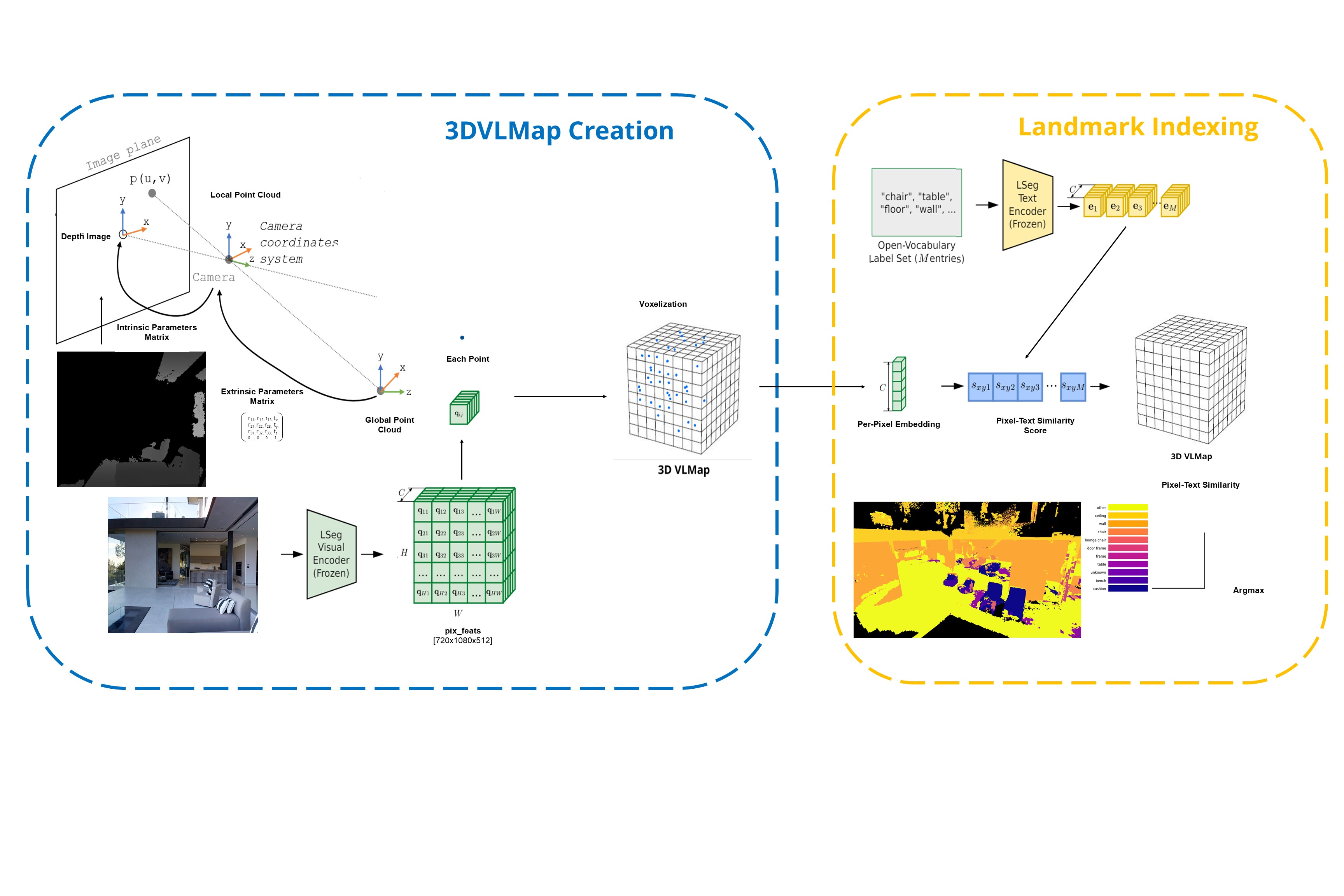
3DVLMaps Approach
3. Evaluation and Results
In the Matterport3D dataset, items are annotated with labeled bounding boxes. To evaluate our 3D segmentation, we compared our semantically labeled voxels to all the voxels that fall inside the objects bounding box, and tracked how many voxels matched / total number of voxels. The couch segmentation example below had an accuracy of 82.7%, and our best class segmentation accuracy was 90.7%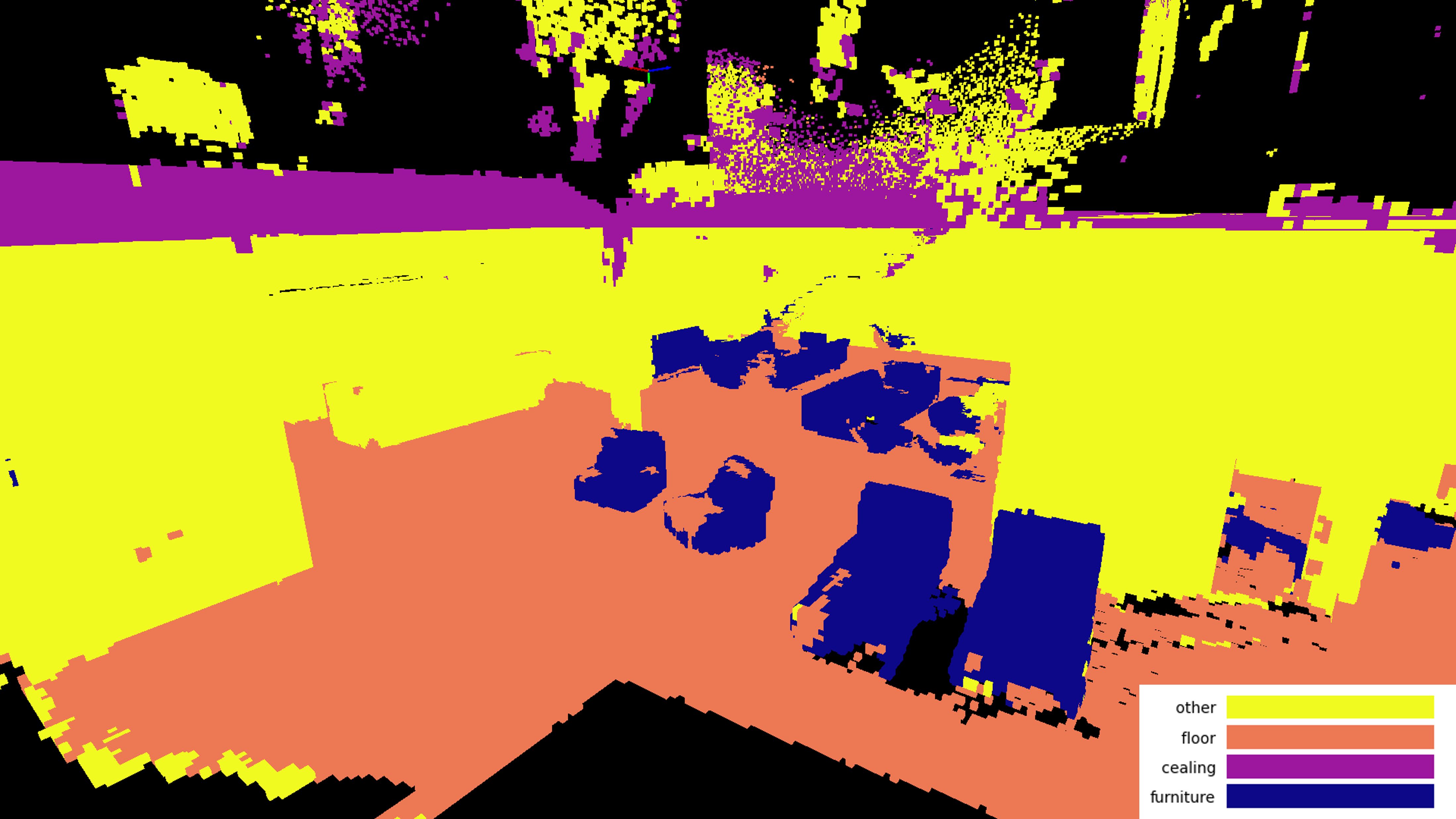
3D Voxel Grid with Open Vocabulary Semantic Features
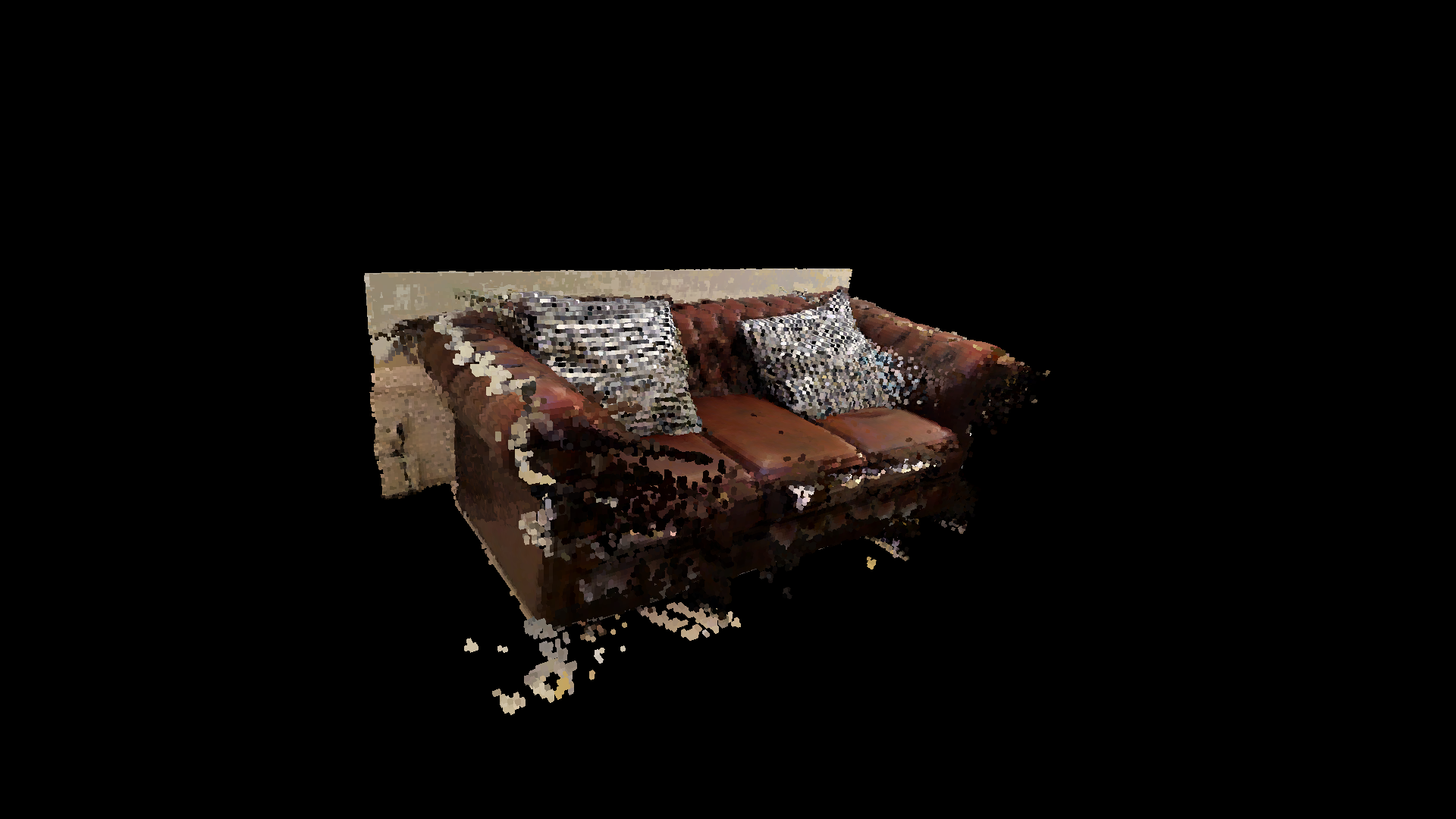

Sofa from Matterport3D Dataset
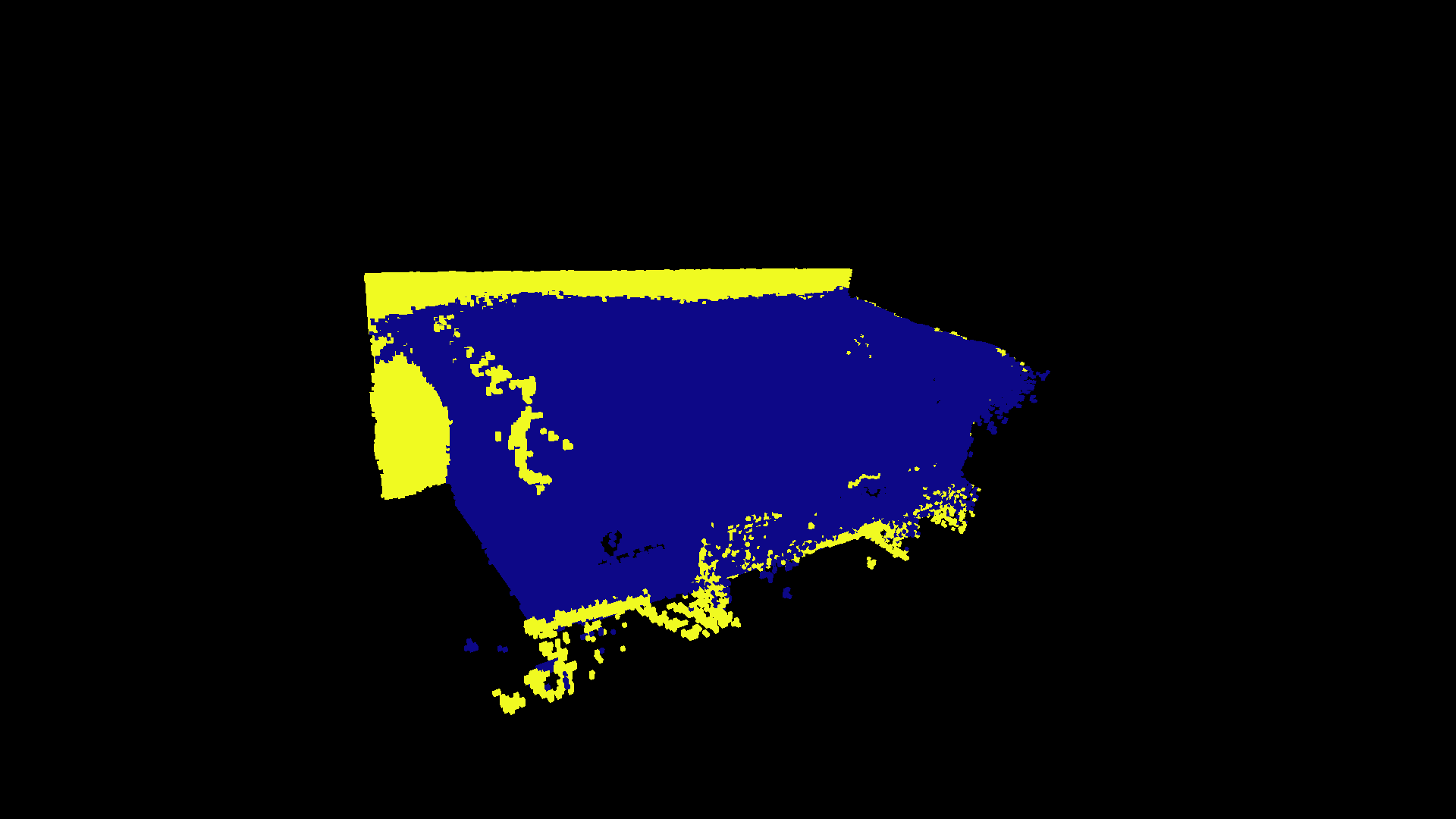
Semantically Embedded Sofa